**본 post는 [인프런 - 스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술]를 참고해 작성했습니다.
프로젝트 생성

- LOMBOK
- Settings -plugin- lombok 검색 실행 (재시작)
- Settings - Annotation Processors 검색 - Enable annotation processing 체크 (재시작)
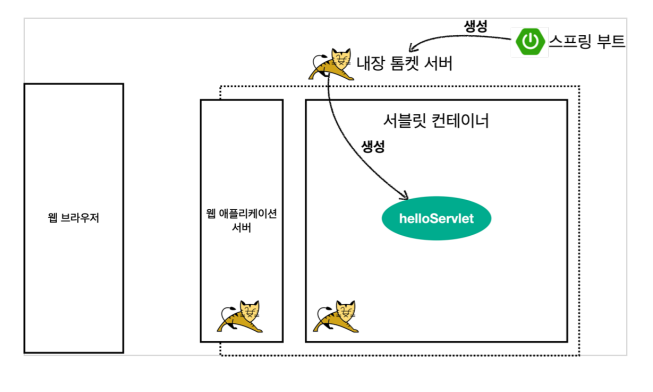
Hello 서블릿
- 서블릿 개념 재정리[서블릿 컨테이너 (WAS)가 하는 일]
- 서블릿 객체를 생성, 초기화, 호출, 종료 (생명주기 관리)
- 서블릿 객체는 싱글톤으로 관리
- 싱글톤
- 객체 1개를 생성하고 공유해서 사용
- 고객의 요청마다 서블릿(객체)를 생성하는 것은 비효율적 ⇒ 최초 로딩 시점에 만들어 두고 재활용
- 고객이 모두 동일한 서블릿 객체 인스턴스에 접근
- : 톰캣서버처럼 서블릿을 지원해주는 서블릿 컨테이너 = WAS
- “톰캣”과 같은 웹 애플리케이션 서버를 직접 설치
- 그 위에 서블릿 코드를 클래스 파일로 빌드해서 올리기
- 톰캣 서버를 실행
= 매우 번거로움
∵ 스프링 부트는 톰캣 서버를 내장 ⇒ 톰캣 서버 설치 없이 편리하게 서블릿 코드를 실행할 수 있음
@WebServlet(name = "helloServlet", urlPatterns = "/hello")
// name = 서블릿 이름
// urlPatterns = URL 매핑(/hello)
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("HelloServlet.service");
System.out.println("request =" + request);
//request =org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade@53712510
System.out.println("response =" + response);
//response =org.apache.catalina.connector.ResponseFacade@7629aa8a
String username = request.getParameter("username");
//?username = yang (파라미터값을 request로 넘김)
System.out.println("username =" + username); //username =yang
response.setContentType("text/plain"); //content-Type
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); //content-Type
response.getWriter().write("hello" + username); //http message body에 들어감
}
}


HttpServletRequest - 개요
- 서블릿은 개발자가 HTTP 요청 메시지를 편리하게 사용할 수 있도록 개발자 대신에 HTTP 요청 메시지를 파싱
- HttpServletRequest 객체에 담아서 제공
[StartLine]
POST /save HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
[Header]
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
[Body]
username=kim&age=20- 임시 저장소 기능
- 저장:
request.setAttribute(name, value) - 조회:
request.getAttribute(name)
- 저장:
- 세션 관리기능
request.getSession(create: true) - 로그인과 같이 유지해야되는 기능
HttpServletRequest - 기본 사용법
f12 network로 header, cookie 등등의 정보를 모두 확인할 수 있음
Http요청 데이터 - 개요
GET - 쿼리파라미터
- /url?username=hello&age=20
- 메시지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- 예) 검색, 필터, 페이징등에서 많이 사용하는 방식
POST - HTML FORM
html 폼을 통해서 전달된 데이터
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 전달 username=hello&age=20
- 예) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용

⇒ 결과적으로, html form이나 get이나 같은 방법으로 진행됨
HTTP message body
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
Http요청 데이터 - GET 쿼리 파라미터
[전체 파라미터 조회]
System.out.println("[전체 파라미터 조회] - start");
//Enumeration<String> parameterNames = request.getParameterNames();
//username, age와 같이 모든 parameter에 대한 값을 꺼낼 수 있음
request.getParameterNames().asIterator()
.forEachRemaining(paramName -> System.out.println(paramName + "=" + request.getParameter(paramName)));
//paramName = parameter명 ex)username, age
//request.getParameter(paramName) = paramName에 해당하는 데이터 요청(꺼내오기)
System.out.println("[전체 파라미터 조회] - end");[단일 파라미터 조회]
System.out.println("[단일 파라미터 조회] - start");
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
System.out.println("name = " + username);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("[단일 파라미터 조회] - end");[복수 파라미터에서 단일 파라미터 조회]
request.getParameterValues()
System.out.println("[이름이 같은 복수 파라미터 조회]");
String[] usernames = request.getParameterValues("username");
for (String name : usernames) {
System.out.println("username = " + name);
}
//[이름이 같은 복수 파라미터 조회]
//username = hello
//username = hello2Http 요청 데이터 - POST HTML Form
application/x-www-form-urlencoded 형식은 앞서 GET에서 살펴본 쿼리 파라미터 형식과 같다.
따라서 쿼리 파라미터 조회 메서드를 그대로 사용하면 된다.
클라이언트(웹 브라우저) 입장에서는 두 방식에 차이가 있지만, 서버 입장에서는 둘의 형식이 동일하므로 request.getParameter() 로 편리하게 구분없이 조회할 수 있다.
정리하면 request.getParameter() 는 GET URL 쿼리 파라미터 형식도 지원하고, POST HTML Form
형식도 둘 다 지원한다.
JSON 일 경우 : application/Json
GET URL 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달할 때는 HTTP 메시지 바디를
사용하지 않기 때문에 content-type이 없다.
POST HTML Form 형식으로 데이터를 전달하면 HTTP 메시지 바디에 해당 데이터를 포함해서 보내기
때문에 바디에 포함된 데이터가 어떤 형식인지 content-type을 꼭 지정해야 한다.
이렇게 폼으로 데이터를 전송하는 형식을 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 라 한다.
⇒ 서버 입장에서는 postman으로 보내도 같은 결과를 반환함
Http 요청 데이터 - API 메시지 바디 - 단순텍스트
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT -
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
- ⇒ 서버-서버 || 서버 - 웹클라이언트 || 웹-앱 등등 다양한곳에서 사용
Http 요청 데이터 - API 메시지 바디 - JSON
JSON형식을 바로 쓰지 않음 ⇒ 객체로 Parsing해서 사용함
- Lombok 을 사용하면 @Getter @Setter을 자동으로 불러올 수 있음
- JSON 결과를 파싱해서 사용할 수 있는 자바 객체로 변환하려면 ⇒ Jackson, Gson같은 JSON 변환 라이브러리 추가해야함
- ⇒ Spring Boot는 자동으로 들어옴(ObjectMapper)
- HTML form 데이터도 meassageBody를 통해 전송되므로 직접 읽을 수 있음
- 그러나, JSON 형식이 아니므로 Parsing은 불가능 !!
request.getParameter(...): 굳이 이렇게 하지 않아도 이 명령어를 쓰면 다 받아올 수 있음 !!

'BACKEND > JAVA & SPRING' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JpaRepository save() (1) | 2023.06.11 |
|---|---|
| DAO DTO Repository (0) | 2023.05.19 |
| JPA (1) | 2023.05.08 |
| [J2KB] 회원관리 (1) | 2023.02.17 |
| [J2KB] API (0) | 2023.02.10 |